Wednesday, June 29, 2011
Comparison of ISP's
I would choose the TPG plan as it is cheaper and has unlimited monthly usage quota aslo fits other requirements.
ISP: TPG
This plan allows unlimited imternet for $29.99. This suited for my requirements as it gives unlimted internet and would cater for my frequent video downloading at a very reasonable price. As there are a no limits so obviously there would not be an extra excess fee. The broadband type for this Plan is ADSL 2+ which is reasnoablly fast.
ISP: Optus
This ISP allows 500 GB of data $99 this plan can suit my requirements as 500 GB a month should be able to cater for frequent downloading of video and if it does pass the 500 GB the there is no excess fee for this; the Internet only slows down. The brodband type of this plan is ADSL 2+ which fairly fast and the price is also somewhat reasonable.
Thursday, June 23, 2011
Synopsis
This short video recounts the story of Buzz Lightyear as he undergoes several processes to locate his lost cookie. Through the use of his detective skills and memory, Buzz interviews potential suspects to find the culprit. Targeting the mass market (general audience), this video demonstrates the relentlessness of individuals when they lose a treasured item and the lengths they would go through to find it.
Tuesday, June 21, 2011
Adobe® Premiere® Pro CS5.5
Featuures:
Flexible, precise, editng tools: widely accepted, customizable NLE shortcuts, powerful trimming and editing tools, has dual system sound suppourt.
Fast realiable mulitscreen delivery: Output your work for computers, smartphones, tablets, and television with Adobe Media Encoder CS5.5. Use intuitive presets and contextual menus to set up sequences once for multiple formats, and batch encode while you keep editing.
Roundtrip workflows with Adobe Audition: Get a fast, flexible roundtrip audio workflow with Adobe Audition CS5.5 software. Pass individual audio clips and multitrack mixes or complete video sequences between Adobe Premiere Pro CS5.5 and Adobe Audition for editing and sweetening.
Flexible, precise, editng tools: widely accepted, customizable NLE shortcuts, powerful trimming and editing tools, has dual system sound suppourt.
Fast realiable mulitscreen delivery: Output your work for computers, smartphones, tablets, and television with Adobe Media Encoder CS5.5. Use intuitive presets and contextual menus to set up sequences once for multiple formats, and batch encode while you keep editing.
Roundtrip workflows with Adobe Audition: Get a fast, flexible roundtrip audio workflow with Adobe Audition CS5.5 software. Pass individual audio clips and multitrack mixes or complete video sequences between Adobe Premiere Pro CS5.5 and Adobe Audition for editing and sweetening.
Direct integration with Adobe Story: Speeds editing workflow by importing scripts with metadata from Adobe Story, an Adobe CS Live online service, into Adobe Premiere Pro CS5.5. Eliminates hours of routine work using Speech Search and other metadata to quickly find footage.
Reviews:
http://www.softwarenewsdaily.com/2011/04/5-reasons-why-i-upgraded-to-adobe-premiere-pro-cs5
http://filmmakingcentral.com/fmc2/2011/05/10/tutorials/premiere-pro-cs5-5-mini-review/
Screen Shots:

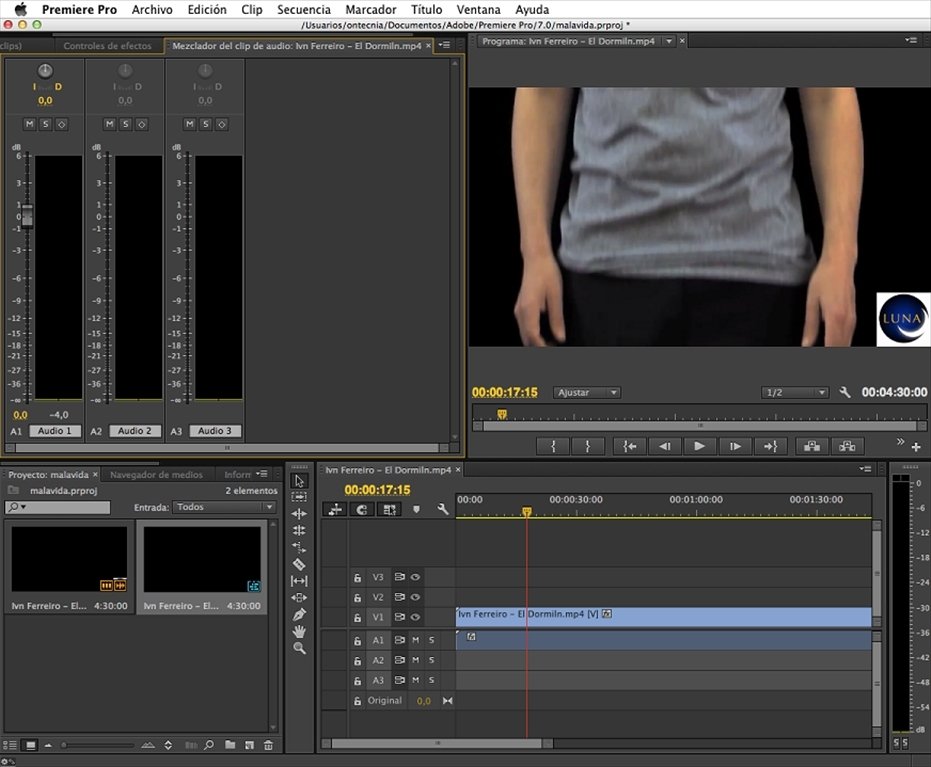
Cost:
$402
Comparison With Widows Live Movie Maker:
Has more advanced editing tools
Fast delivery
Has roundtrip work flow
Faster editing work flow
Not free
Reviews:
http://www.softwarenewsdaily.com/2011/04/5-reasons-why-i-upgraded-to-adobe-premiere-pro-cs5
http://filmmakingcentral.com/fmc2/2011/05/10/tutorials/premiere-pro-cs5-5-mini-review/
Screen Shots:


Cost:
$402
Comparison With Widows Live Movie Maker:
Has more advanced editing tools
Fast delivery
Has roundtrip work flow
Faster editing work flow
Not free
Corel® VideoStudio® Pro X4
Features:
Stop Motion Animation – create your own animated movie starring people, toys or objects
Flexible workspace – drag to resize and move panels, even across two monitors
Time-Lapse Effect – easily and quickly create time-lapse sequences from photos or videos
Advanced editing – have fun making movies with quick access to professional editing tools
Export in 3D – turn your 2D video into a 3D movie
Easy HD sharing – author and burn HD movies directly to DVD and Blu-ray Disc™
Online sharing – upload movies directly to YouTube™, Vimeo®, Flickr®, Facebook® and other websites
Reviews:
http://www.goodgearguide.com.au/review/software_and_services/corel/videostudio_pro_x4/382322
http://www.myeasydata.com/corel-video-studio-pro-x4-review.html
Screen Shots:
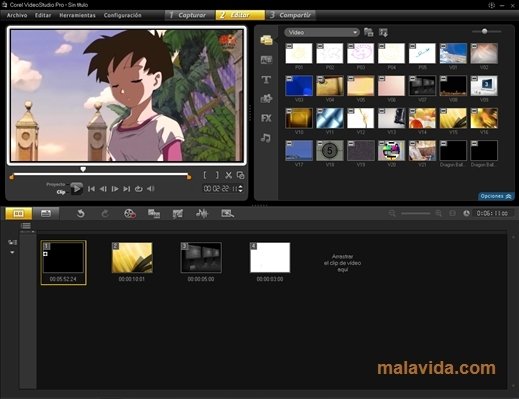

Cost:
$149.00
Comparison with windows live movie movie maker:
This has more flexible work space
Has more advanced and professional editing tools
Allows to export in 3 dimensional format
Easier HD sharing
It is not free
Stop Motion Animation – create your own animated movie starring people, toys or objects
Flexible workspace – drag to resize and move panels, even across two monitors
Time-Lapse Effect – easily and quickly create time-lapse sequences from photos or videos
Advanced editing – have fun making movies with quick access to professional editing tools
Export in 3D – turn your 2D video into a 3D movie
Easy HD sharing – author and burn HD movies directly to DVD and Blu-ray Disc™
Online sharing – upload movies directly to YouTube™, Vimeo®, Flickr®, Facebook® and other websites
Reviews:
http://www.goodgearguide.com.au/review/software_and_services/corel/videostudio_pro_x4/382322
http://www.myeasydata.com/corel-video-studio-pro-x4-review.html
Screen Shots:

Cost:
$149.00
Comparison with windows live movie movie maker:
This has more flexible work space
Has more advanced and professional editing tools
Allows to export in 3 dimensional format
Easier HD sharing
It is not free
Thursday, June 16, 2011
transferring video from my phone to computers
The steps involved:

- Connect USB cable onto phone and the other end in the USB port.
- Auto play should come up. Click option that says "open device to view files" or click start>computer and it should be there
- Than copy video from folder that says "DCIM" than the folder that says "camera" to the desired location on the computer.
My phone stores videos and audio in 3GPP format
Picture of phone:

Wav, mp3, aiff
Wav:
WAV is an audio file format that was developed by Microsoft. It is so wide spread today that it is called a standard PC audio file format. A Wave file is identified by a file name extension of WAV (.wav) This allows content developers to freely move audio files between platforms for processing, this file format stores information about the file's number of tracks (mono or stereo), sample rate, bit depth, as well as the uncompressed raw audio data.
mp3:
WAV is an audio file format that was developed by Microsoft. It is so wide spread today that it is called a standard PC audio file format. A Wave file is identified by a file name extension of WAV (.wav) This allows content developers to freely move audio files between platforms for processing, this file format stores information about the file's number of tracks (mono or stereo), sample rate, bit depth, as well as the uncompressed raw audio data.
mp3:
The name of the file extension and also the name of the type of file for MPEG, audio layer 3. Layer 3 is one of three coding schemes (layer 1, layer 2 and layer 3) for the compression of audio signals. Layer 3 uses perceptual audio coding and psychoacoustic compression to remove all unnecessary information . It also adds a MDCT (Modified Discrete Cosine Transform) that implements a filter bank, increasing the frequency resolution 18 times higher than that of layer 2.The result in real terms is layer 3 shrinks the original sound data from a CD(with a bit rate of 1411.2 kilobits per one second of stereo music) by a factor of 12 (down to 112-128kbps) without sacrificing sound quality.
Aiff:
Short for Audio Interchange File Format, a common format for storing and transmitting sampled sound. The AIFF format does not support data compression so AIFF files tend to be large. However, there is another format called AIFF-Compressed (AIFF-C orAIFC) that supports compression ratios as high as 6:1.
Short for Audio Interchange File Format, a common format for storing and transmitting sampled sound. The AIFF format does not support data compression so AIFF files tend to be large. However, there is another format called AIFF-Compressed (AIFF-C orAIFC) that supports compression ratios as high as 6:1.
Decibel
The decibel (abbreviated dB) is the unit used to measure the intensity of a sound. also known as a logarithmic unit of sound intensity; 10 times the logarithm of the ratio of the sound intensity to some reference intensity
Hertz
Abbreviated as Hz is a unit of frequency of electrical vibrations equal to one cycle per second. The Hertz is named after Heinrich Hertz, who first detected electromagnetic waves.
Frequency
Audio frequency represent the range of signals that are audible to the human ear. The range of audio frequencies is usually considered to be in the region between 20 and 20,000 hertz. It is the property of sound that most determines pitch.
Track
A track is a single stream of any audio which contains channel(s) Digital audio tracks let you store audio data as digital sound values rather than as musical symbols.A digital audio track works like a recording tape that you can include in a musical document and on which you can record whatever you want for subsequent playback.


Channel
Channel is one individual audio track. A channel is just one separate stream of audio information. There is only one channel in mono audio sources. More commonly, there are sources that hold two channels - stereo sources. Sources with more than two channels are referred to as multichannel.
Stereo
Audio stereo means sound which is divided into two separate channels. These two channels are played back at the same time through separate speakers. The effect is to create a fuller sound, and provide the ability to mix certain sounds between channels.
Some examples:- Spreading the instruments in a music track from left to right. Often the tom-toms in a drum kit provide great stereo panning, as do some guitar effects.
- Following the action in a video, e.g. a car speeds across the screen as the audio pans with it.
Wednesday, June 15, 2011
Name Lossy file formats for audio, still image and video format.
Audio:
AAC - .mp4 .m4a .3gp
ATRAC - .oma .aa3
MP3 - .mp3
MPEG-1 - .mp2
Musepack - .mpc .mpp
WMA - .wma
Still Image:
CPC - .cpc
DjVu - .djvu .djv
JPEG - .jpg .jpeg
Video:
DV - .dv .dif
MNG - .mng
MPEG-1 - .mpg .mpeg .mp2 .mp3 .mpa
MPEG-2 - .mpg .mpeg .mp2 .mp3 .m2v
Ogg Theora - .ogv
Why is human psychology and perception an important factor in methods of Lossy compression?
This is because in lossy compressions, very little of the information from a file is still there. Without the deception of how the human eye sees the difference of information, the file would be very different from the original. If we allow our mind to do so would be able to the errors in a lossy compression.
Which method offers the greatest compression ratio?
The method that offers the greatest compression ratio is lossy compression. The compression ratio of lossy video codecs are generally better than audio and still-image.
The video can be compressed at a 100:1 ratio
Audio can often be compressed at a 10:1
Still images are also often compressed at a 10:1 ratio.
The compression rate of lossy compression is about 5-6% while the rate of lossless compression ranges from 50 60%.
The video can be compressed at a 100:1 ratio
Audio can often be compressed at a 10:1
Still images are also often compressed at a 10:1 ratio.
The compression rate of lossy compression is about 5-6% while the rate of lossless compression ranges from 50 60%.
What is the difference between Lossy and Lossless data compression?
Lossy compression technologies attempt to eliminate redundant or unnecessary information. Most video compression technologies, such as MPEG, use a lossy technique.
lossless compression refers to data compression techniques in which no data is lost. For most types of data, lossless compression techniques can reduce the space needed by only about 50%
Why is data compression an important technique for the online world?
Data compression is very important for the online world. When you visit a website, all the picture files that are downloaded are all compressed. This also includes videos when online.
Files that are fairly can be compressed so that they are smaller in size. making it more efficient when downloading or uploading.
Files that are fairly can be compressed so that they are smaller in size. making it more efficient when downloading or uploading.
What is Data Compression?
Data compression is basically storing data in a format that requires less space than usual. It is the process of encoding information such as videos, images and audios in fewer bits than its original. It reduces size as well as quality of data.
What is a data compression ratio?
You can set the compression ratio for color scanned data. A high compression ratio reduces the data size, but results in low quality images. On the contrary, a low compression ratio increases the data size, but results in high quality images.
Tuesday, June 7, 2011
What is meant by “generation loss”, where does it happen?
Generation loss refers to the loss of quality and potential increase of file size between subsequent copies of data. Anything that reduces the quality of the representation when copying, and would cause further reduction in quality on making a copy of the copy, can be considered a form of generation loss.
In analog systems (including systems that use digital recording but make the copy over an analog connection), generation loss is mostly due to noise and bandwidth issues in cables, amplifiers, mixers, recording equipment and anything else between the source and the destination. Poorly adjusted distribution amplifiers and mismatched impedances can make these problems even worse. Repeated conversion between analog and digital can also cause loss.
In analog systems (including systems that use digital recording but make the copy over an analog connection), generation loss is mostly due to noise and bandwidth issues in cables, amplifiers, mixers, recording equipment and anything else between the source and the destination. Poorly adjusted distribution amplifiers and mismatched impedances can make these problems even worse. Repeated conversion between analog and digital can also cause loss.
Describe what a codec is.
Codec is a short name for coder-decoder, the software that takes a raw data file and turns it into a compressed file. Because compressed files only contain some of the data found in the original file, the codec is the necessary “translator” that decides what data makes it in to the compressed version and what data gets discarded.
Different codecs translate in different ways, so a video file compressed using the Intel Indeo codec will be different from a file compressed using the Cinepak codec, for example. Sometimes the difference is noticeable, sometimes not, but it’s good to be aware of what codecs are best for what you’re trying to do in order to maintain the best ratio of file size to quality.
Different codecs translate in different ways, so a video file compressed using the Intel Indeo codec will be different from a file compressed using the Cinepak codec, for example. Sometimes the difference is noticeable, sometimes not, but it’s good to be aware of what codecs are best for what you’re trying to do in order to maintain the best ratio of file size to quality.
Why do digital video cameras use video compression
Many types of video compression exist for serving digital video over the internet and on optical disks. The file sizes of digital video used for professional editing are generally not practical for these purposes, and the video requires further compression with codecs such as the Windows Media format, MPEG2, MPEG4, Real Media, and more recently H.264. Probably the most widely used formats for delivering video over the internet are MPEG4 and Windows Media, while MPEG2 is used almost exclusively for DVDs, providing an exceptional image in minimal size but resulting in a high level of CPU consumption to decompress.
What is an IEEE 1394 port
IEEE 1394, also known as FireWire,originated from Apple which, like USB, allows the connection of peripherals to a computer.IEEE 1394 supports much higher bandwidth than USB, allowing you to get feed from a high-resolution video camera onto a computer without experiencing issues. Today, IEEE 1394 has become a computing standard for high-bandwidth devices
IEEE 1394 works through peer-to-peer networking, meaning that devices can connect and talk to each other without needing a computer. IEEE 1394 has the capability of plug-and-play. This means that a device connected to a computer is detected without need of a driver disk or other software.
IEEE 1394 works through peer-to-peer networking, meaning that devices can connect and talk to each other without needing a computer. IEEE 1394 has the capability of plug-and-play. This means that a device connected to a computer is detected without need of a driver disk or other software.
Monday, June 6, 2011
PAL, NTSC, and SECAM,
Pal: short for Phase Alternating Line, is the analogue video format.The name "Phase Alternating Line" describes the way that part of the colour information on the video signal is reversed in phase with each line, which automatically corrects phase errors in the transmission of the signal.
NTSC: The National Television Standards Committee The NTSC format consists of 29.97 interlaced frames of video a second, each consisting of 480 lines of vertical resolution out of a total of 525 (the rest are used for sync, vertical retrace, and other data such as captioning)
Secam: (Sequentiel Couleur avec Mémoire, French for "sequential color with memory") is an analog television system, using frequency modulation to encode chrominance information. It is so named because it uses memory to store lines of color information, in order to eliminate the color artifacts found on systems using the NTSC standard.
NTSC: The National Television Standards Committee The NTSC format consists of 29.97 interlaced frames of video a second, each consisting of 480 lines of vertical resolution out of a total of 525 (the rest are used for sync, vertical retrace, and other data such as captioning)
Secam: (Sequentiel Couleur avec Mémoire, French for "sequential color with memory") is an analog television system, using frequency modulation to encode chrominance information. It is so named because it uses memory to store lines of color information, in order to eliminate the color artifacts found on systems using the NTSC standard.
What is the colour system called RGB
It is an additive colour system involves light emitted directly from a source, before an object reflects the light. The additive reproduction process mixes various amounts of red, green and blue light to make other colors.
Combining one of these additive primary colors with another produces the additive secondary colors cyan, magenta, yellow. Mixing all three primary colors produces white.
 To illustrate additive color, imagine three spotlights, one red, one green and one blue focused from the back of an ice arena on skaters in an ice show. Where the blue and green spotlights overlap, the color cyan is produced; where the blue and red spotlights overlap, the color magenta is produced; where the red and green spotlights overlap the color yellow is produced. When added together, red, green and blue lights produce what we perceive as white light
To illustrate additive color, imagine three spotlights, one red, one green and one blue focused from the back of an ice arena on skaters in an ice show. Where the blue and green spotlights overlap, the color cyan is produced; where the blue and red spotlights overlap, the color magenta is produced; where the red and green spotlights overlap the color yellow is produced. When added together, red, green and blue lights produce what we perceive as white light
Combining one of these additive primary colors with another produces the additive secondary colors cyan, magenta, yellow. Mixing all three primary colors produces white.
Television and computer monitors create color using the primary colors of light. Each pixel on a monitor screen starts out as black. When the red, green and blue phosphors of a pixel are illuminated simultaneously, that pixel becomes white. This known as additive color.
 To illustrate additive color, imagine three spotlights, one red, one green and one blue focused from the back of an ice arena on skaters in an ice show. Where the blue and green spotlights overlap, the color cyan is produced; where the blue and red spotlights overlap, the color magenta is produced; where the red and green spotlights overlap the color yellow is produced. When added together, red, green and blue lights produce what we perceive as white light
To illustrate additive color, imagine three spotlights, one red, one green and one blue focused from the back of an ice arena on skaters in an ice show. Where the blue and green spotlights overlap, the color cyan is produced; where the blue and red spotlights overlap, the color magenta is produced; where the red and green spotlights overlap the color yellow is produced. When added together, red, green and blue lights produce what we perceive as white light
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)